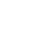What is Fiber Polypropylene and How is it Used?
Fiber Polypropylene has gained attention in various industries due to its unique properties. According to Dr. Emily Parker, an expert in synthetic materials, "Fiber Polypropylene stands out for its lightweight and durability." This highlights its growing importance in applications such as automotive, textiles, and construction.
The versatility of Fiber Polypropylene makes it a popular choice. Its resistance to moisture and chemicals boosts performance in challenging environments. For instance, in the car manufacturing industry, it is often used in interior components. The fiber’s ability to maintain shape under stress is crucial for vehicle safety.
However, not all uses are perfect. Challenges remain in recycling and environmental impact. Many manufacturers are exploring sustainable options. The journey of Fiber Polypropylene continues, revealing both potential and areas for improvement. As its demand increases, the industry must address these issues carefully.

What is Fiber Polypropylene and Its Chemical Composition?
Fiber polypropylene is a type of plastic derived from propylene monomers. It is part of the polyolefin family, widely appreciated for its versatility. The chemical composition includes repeating units of propylene, contributing to its strength and flexibility. This material is lightweight yet durable, making it suitable for various applications.
The production process involves polymerization, where propylene gas is converted into long chains. These chains create fibers that can be woven or knitted. The fibers offer resistance to moisture and chemicals, often outperforming natural fibers in specific scenarios. However, its durability sometimes raises concerns about environmental impact. Efforts are underway to address these issues.
Applications of fiber polypropylene range from textiles to industrial uses. It is commonly found in bags, carpets, and non-woven fabrics. Despite its usefulness, the question of sustainability looms large. Consumers and manufacturers must reflect on the lifecycle of these products. Awareness of recycling options can help mitigate some environmental concerns associated with polypropylene usage.
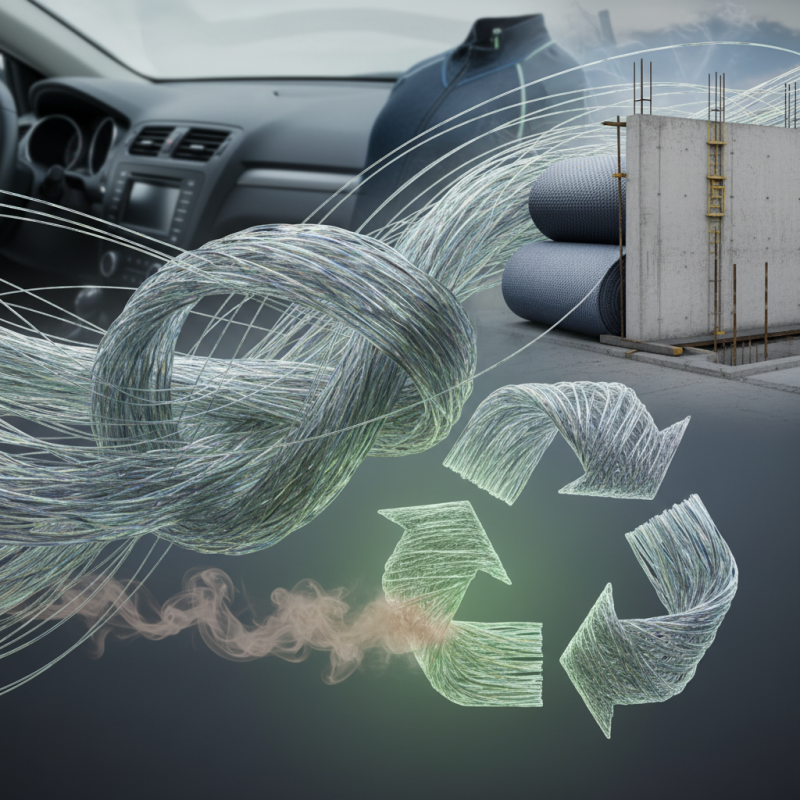
Key Properties of Fiber Polypropylene in Various Applications
Fiber polypropylene is a versatile material known for its unique properties. It is lightweight yet durable, making it suitable for various applications. Its resistance to moisture and chemicals enhances its usability in harsh environments. This fiber is often used in textiles, automotive parts, and construction materials.
In textiles, fiber polypropylene provides breathability and comfort. This makes it popular for apparel and outdoor gear. However, some users find it less flexible than other fibers.
In automotive applications, it helps reduce weight while maintaining strength. But, there are concerns about its long-term durability under UV exposure.
Fiber polypropylene is also favored in geotextiles. It stabilizes soil and controls erosion effectively. Yet, its environmental impact raises questions. As it is not biodegradable, the industry is challenged to develop sustainable alternatives. Balancing performance and environmental responsibility remains a key issue for future developments.
Industry Applications: Where is Fiber Polypropylene Used?
Fiber polypropylene is widely used across various industries due to its unique properties. In textiles, it is favored for making carpets and upholstery. This fiber is lightweight and resistant to stains. As a result, products made from fiber polypropylene maintain their appearance over time, but are not immune to wear and tear.
In construction, fiber polypropylene serves as a reinforcement material. It enhances the strength of concrete, making it more durable. However, some studies suggest that the environmental impact of disposal might be significant. In automotive manufacturing, it is used for interior components thanks to its lightweight nature and resistance to moisture. While its benefits are clear, manufacturers must consider the balance of performance against sustainability.
Agriculture also leverages this fiber for landscaping and erosion control. Geotextiles made of fiber polypropylene are effective but can be less biodegradable. The durability is a double-edged sword. On one hand, it aids in effective ground cover; on the other, it may contribute to long-term waste. Each application illustrates the dual nature of fiber polypropylene's impact on various sectors.
Comparative Analysis: Fiber Polypropylene vs. Other Synthetic Fibers
Fiber polypropylene is gaining attention as a versatile synthetic fiber. It's lightweight and resistant to moisture. Compared to other synthetic fibers, it has unique properties. For instance, it's less absorbent than nylon. This means it dries faster, making it ideal for various applications.
When analyzing fiber polypropylene against materials like polyester or rayon, some differences emerge. Polyester is generally stronger, but it can trap moisture. Fiber polypropylene, on the other hand, allows easier breathability. However, it may not match the durability of nylon in high-stress situations. This disparity often leads to reconsideration of fiber choice based on specific requirements.
While fiber polypropylene is impressive, it has limitations too. Its low UV resistance affects outdoor usage. In contrast, other fibers may offer better longevity against sun damage. This knowledge is crucial when selecting materials for varied environments. Overall, fiber polypropylene presents both advantages and challenges in the synthetic fiber landscape.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Fiber Polypropylene
Fiber polypropylene is a versatile material gaining traction across various industries. Its lightweight and durable properties make it ideal for multiple applications. However, the environmental impact of fiber polypropylene raises questions about sustainability.
The production of fiber polypropylene results in significant greenhouse gas emissions. A study by the Environmental Protection Agency indicates that plastics contribute nearly 15% of global methane emissions. Once discarded, fiber polypropylene can take hundreds of years to decompose. Such a long lifespan raises concerns about landfill congestion and plastic pollution in oceans.
Tip: Consider recycling or reusing fiber polypropylene products wherever possible. It helps reduce waste and minimizes environmental harm.
On the other hand, innovations in recycling methods are emerging. Chemical recycling processes could transform used fiber polypropylene into new raw materials. This change can significantly lower resource consumption. A report from the International Journal of Environmental Research shows that recycling polypropylene can reduce energy use by up to 90%. Nonetheless, the current infrastructure for recycling remains inadequate. Many facilities are not equipped to handle such materials effectively.
Tip: Support local initiatives aimed at improving recycling programs. Your involvement can drive change and promote sustainability.
What is Fiber Polypropylene and How is it Used? - Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Fiber Polypropylene
| Aspect | Description | Environmental Impact | Sustainability Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Fiber polypropylene is a type of synthetic polymer derived from petroleum. | High carbon footprint due to petroleum extraction and processing. | Use of recycled polypropylene helps reduce environmental impact. |
| Applications | Used in textiles, packaging, automotive components, and geotextiles. | End-of-life disposal can lead to pollution if not properly managed. | Development of biodegradable alternatives and recycling programs. |
| Durability | Known for its strength and resistance to chemicals and moisture. | Longevity contributes to waste management challenges. | Encouraging reusability of products made from fiber polypropylene. |
| Recyclability | Can be recycled but often not returned to the market. | Contributes to landfill issues if improperly recycled. | Awareness programs for proper disposal and recycling techniques. |
Related Posts
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Fiber Polypropylene Products for Your Business Needs
-

Exploring Alternative Options: The Top Choices for Heavy Periods Beyond Traditional Sanitary Towels
-

Understanding Polyester Staple: The Key Ingredient in a $540 Billion Global Textile Industry
-
2025 Top Trends in Polyester Staple: Innovations and Applications
-

The Future of Sustainable Water and Sanitation Solutions
-

Unlocking the Secrets of Iec Material: Essential Insights on Water and Sanitation Management